Replication and Prediction in SimpleGAS
The Golden Rule: Server Authority
In SimpleGAS, the server is always the ultimate authority. This means:
- The server decides what’s “real” in your game
- Clients can propose or predict what happens, but the server gets final say
- If there’s a conflict between client and server, the server wins
This approach prevents cheating and keeps your game consistent across all players, but it creates a challenge: lag. Players hate waiting for server confirmation before seeing their actions take effect.
That’s where prediction comes in!
Abilities: Synchronized Actions
How Abilities Replicate
When a player activates an ability (like casting a fireball), SimpleGAS creates an AbilityState struct:
struct FAbilityState
{
FGuid AbilityID; // Unique identifier
TSubclassOf<USimpleAbilityBase> AbilityClass; // What ability is this?
double ActivationTimeStamp; // When was it activated?
FInstancedStruct ActivationContext; // Extra data passed at activation
EAbilityStatus AbilityStatus; // Is it running, ended, canceled?
TArray<FSimpleAbilitySnapshot> SnapshotHistory; // Record of state changes
};
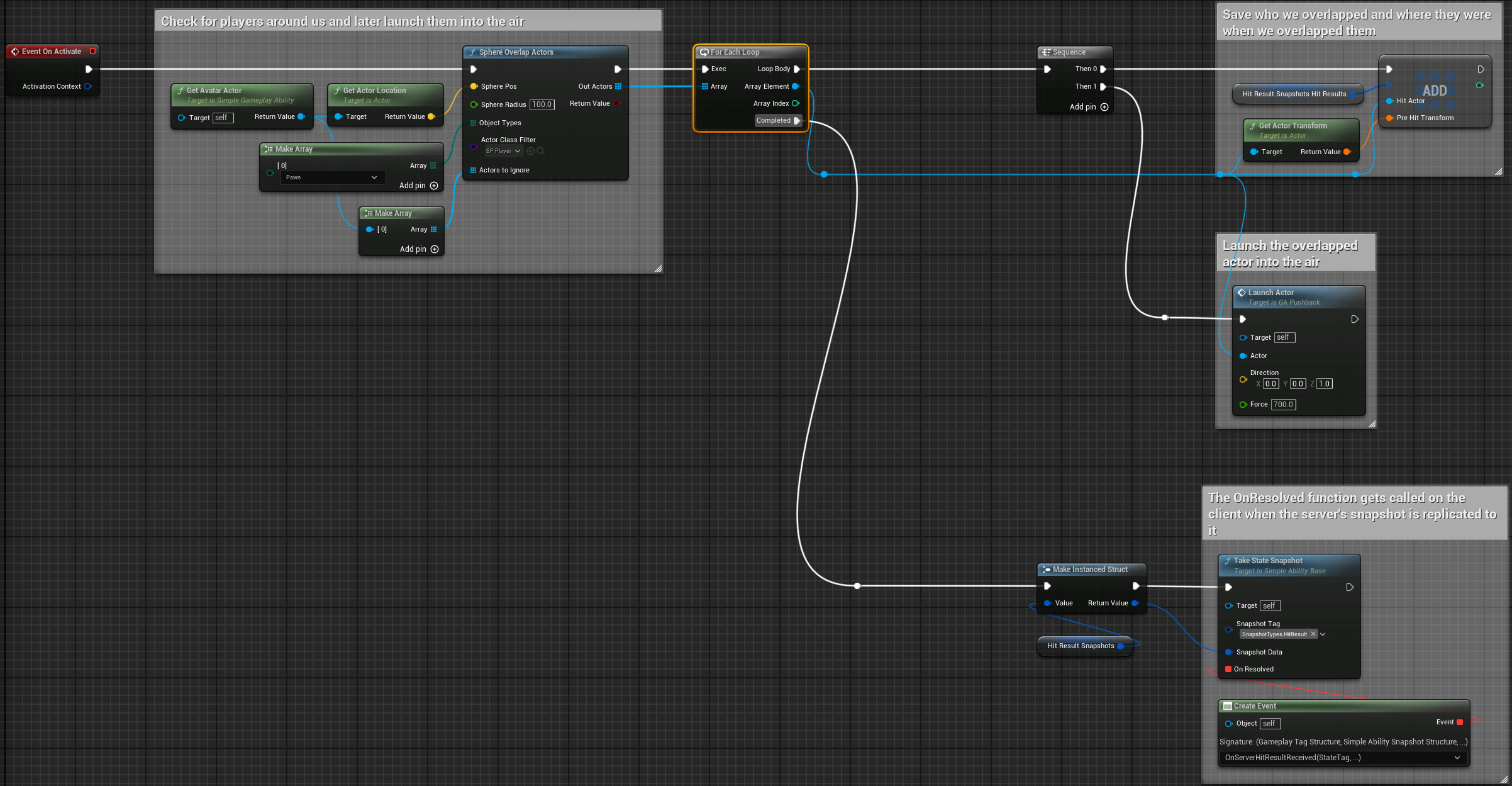
For server-initiated abilities, the flow works like this:
- Client requests ability activation
- Server validates and creates an authoritative AbilityState
- This AbilityState gets replicated to clients via
AuthorityAbilityStates - Clients receive the AbilityState and activate their local version
SimpleGAS handles all this synchronization automatically. Your ability classes define the behavior, and the AbilityComponent manages the replication.
Client Prediction: Instant Feedback
But waiting for the server feels sluggish, especially with high ping. That’s why SimpleGAS supports client prediction:
- Client immediately activates ability locally (feels snappy!)
- Client sends activation request to server
- Server validates and activates its authoritative version
- Server replicates back the “official” state
- Client compares its predicted version against server’s version
- If they match, great! If not, client corrects itself
This is controlled through the ActivationPolicy property on abilities:
Replicated:
ClientPredicted: Run on client immediately, correct if server disagrees
ServerInitiatedFromClient: Request from client, but wait for server to activate first
ServerAuthority: Can only activate on server but still replicate to clients
Non Replicated:
LocalOnly: Can activate on client or server, but no replication
ClientOnly: Can only activate on client
ServerOnly: Can only activate on server
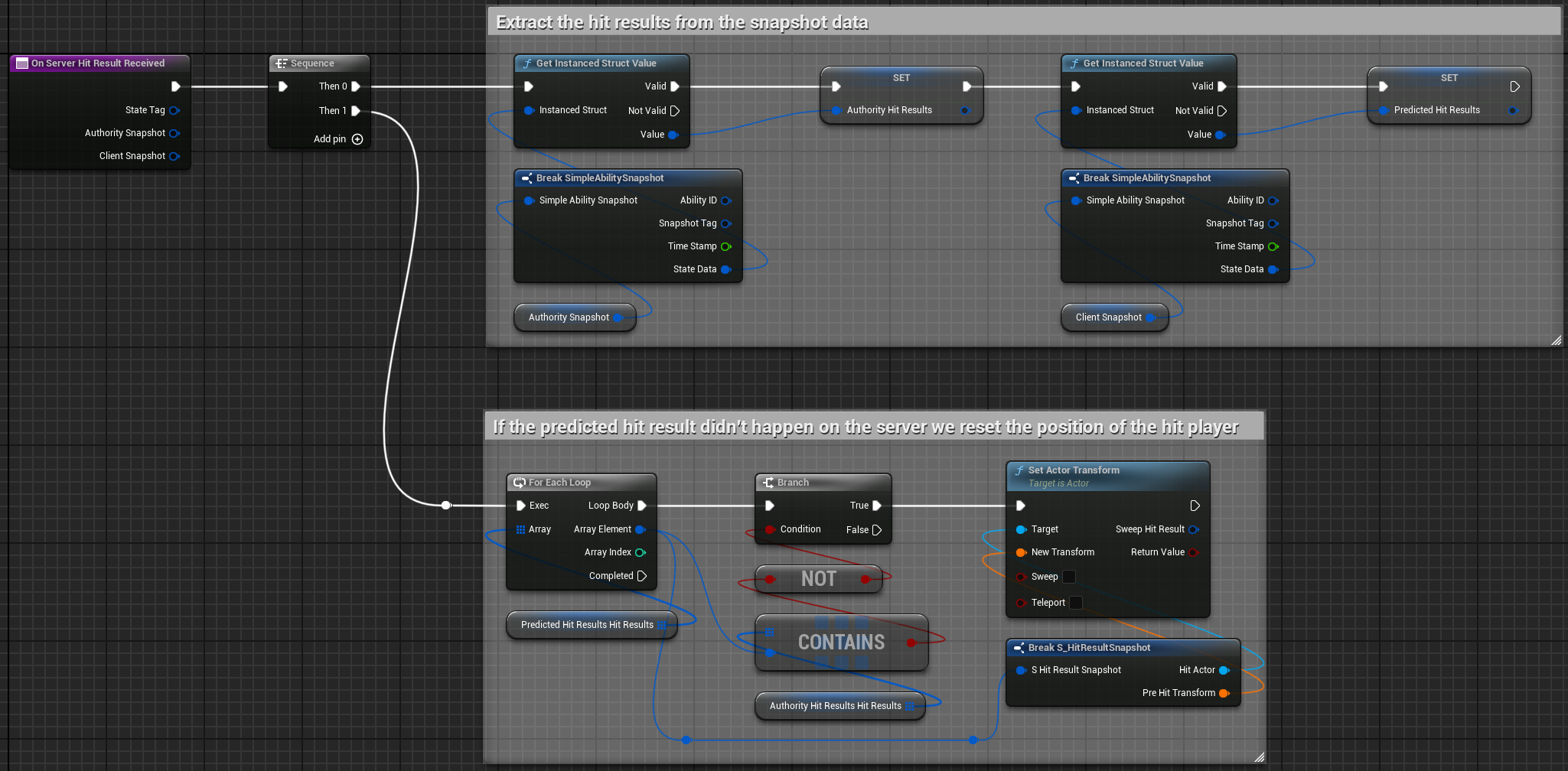
State Snapshots: Tracking What’s Important
During an ability’s lifecycle, important moments can be captured as “snapshots” with TakeStateSnapshot() and a custom struct:
Attributes: Synchronized Stats
Attributes like health, stamina, or speed use a similar strategy:
- Server maintains authoritative attributes in
AuthorityFloatAttributesandAuthorityStructAttributes - Client keeps local copies in
LocalFloatAttributesandLocalStructAttributes - When server changes attributes, changes are replicated to clients
This parallel structure means:
- Server always has the final say on attribute values
- Clients have immediate access to read attributes
- When replicated values arrive, clients update their local copies
Behind the scenes, SimpleGAS handles this with FFastArraySerializer to efficiently replicate only changed attributes.
Attribute Modifiers: Smart Effects
Attribute modifiers (like damage-over-time effects or buffs) are specialized abilities that modify attributes. They follow similar replication rules, with some automation for convenience:
- Modifiers can be client-predicted using
ModifierApplicationPolicy - The side effects (VFX, sounds, activated abilities) get cleaned up automatically if the server rejects the modifier
- Predictive modifiers show immediate feedback but correct themselves if invalid
Example: When a player hits an enemy with fire damage:
1. Client shows immediate hit effect and reduces enemy health
2. Server validates hit and replicates official damage
3. If client and server agree, nothing changes visually
4. If client was wrong, health bar "springs back" and effects are removed
This automatic handling means you don’t need to manually reconcile prediction errors for modifiers - the system cleans up predicted effects that didn’t actually happen.
FInstancedStruct: Flexible Data Replication
SimpleGAS uses FInstancedStruct to replicate dynamic data:
- Allows arbitrary structs to be replicated
- Lets you pass any data structure through the network
However, keep these things in mind:
- Struct properties must be replicable types
- Complex nested structs can be bandwidth-intensive
When using FInstancedStruct in your abilities:
- Keep payloads as small as practical
- Use basic types where possible